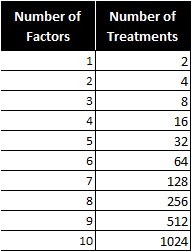
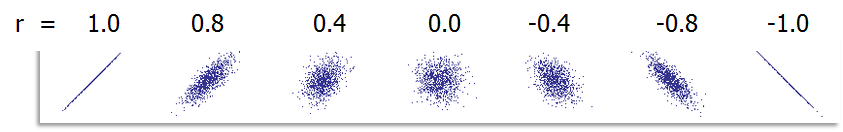
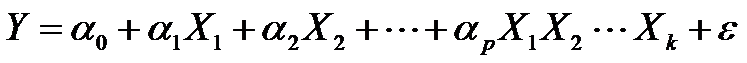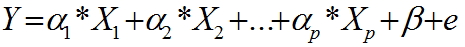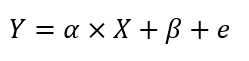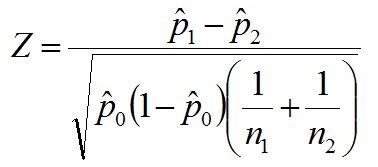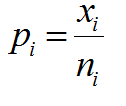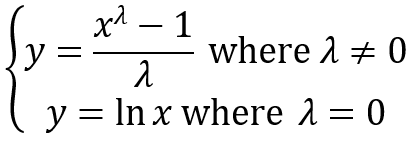What Are Fractional Factorial Experiments? In simple terms, a fractional factorial experiment is a subset of a full factorial experiment. Why Fractional Factorial Experiments? To run a full factorial experiment for k factors, we need 2k unique treatments. In other words, we need resources that can afford at least 2k runs. With k increasing, the […]